How do mobile networks work?
Mobile, or ‘cellular’, networks operate through fixed location transceivers (radio towers) delivering ‘spectrum’, which is the technical term for the radio waves that provide the data packets that enable your smartphone to connect with and transfer data to and from the internet. Keep reading to learn about the specific types of mobile data connections in our handy mobile network guide.
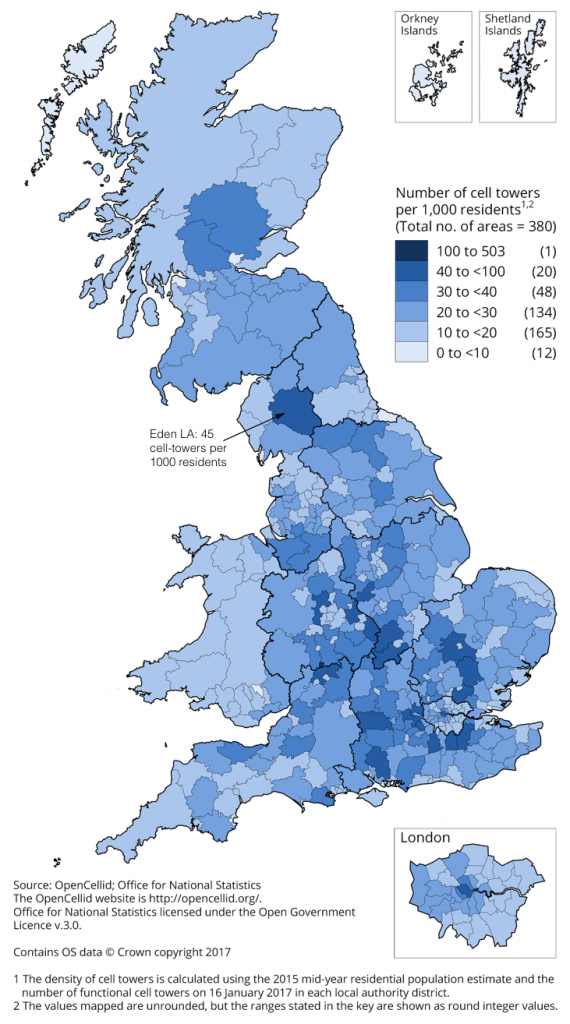
There are 1,427,795 cell towers helping mobile networks work, and that’s only those officially registered with the OpenCellID database in the UK; all of which work to provide coverage over the widest possible geographical area, often by overlapping in areas of particularly high concentration of use. The below graph illustrates the concentration of cell towers per 1000 residents in the UK, sourced from the Office for National Statistics.
Click the link for Unbeatable Mobile Phone Deals You Won't Want to Miss!
--------------------------------------------
Mobile Network Guide: What is the difference between 3G, H+, 4G, LTE, 5G?
GPRS
GPRS, or ‘General Packet Radio Service’ is a packet oriented mobile data standard established by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute. It is a ‘best effort’ service which means that a constant standard of performance cannot be promised, as network latency will depend on how many mobile phones are taking advantage of mobile networks at any one time.
In simple terms: GPRS is essentially the most basic network standard that your phone may still default back to when you have a distinct lack of signal or use your device in an extremely busy area. Comparing GPRS to the speed of our current mobile technology is a great reminder of the exponential increases in technological advancement we have had in recent times.

An old GPRS modem
By Korax1214 – Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3903260
GSM
GSM, Global System for Mobile Communications, similar to GPRS, is a standard of mobile network established by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute which established the protocols for second generation mobile networks, known commonly as ‘2G’.
Simply put: GSM represents the new standards introduced with 2G replacing 1G networks. One example of these new standards includes data transfer changing from circuit-switched transport to packet data transport, which remains the standard method by which mobile data operates.
The UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service) is a mobile cellular system established bsaed on the GSM standard that offered gerater spectral efficiency and bandwidtch to providers of mobile networks.
See our article on fixed GSM phones.

You might recognise this symbol
E / EDGE
Often shown on mobile devices as ‘E’ when in use, the EDGE technology stands for ‘Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution’ and represents the continued evolution of the 2G mobile networks as technology transitioned into 3G performance.
Often considered ‘2.75G’, EDGE allowed for improved data transmission rates, resulting in network capacity and performance increasing 300%, thus the name ‘GSM evolution’ as EDGE bridged the gap between GSM and 3G.
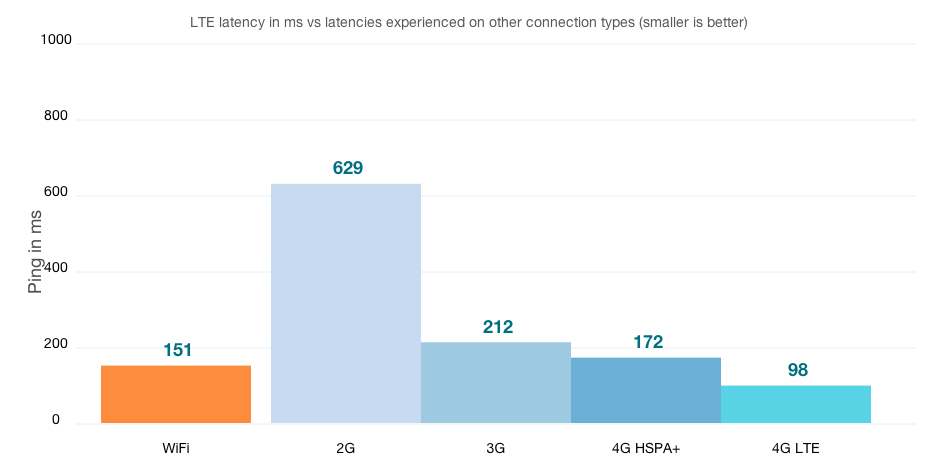
This graph demonstrates the drastic improvements that came with 3G
https://www.cablefree.net/wirelesstechnology/4glte/lte-network-latency/
3G
You are most likely familiar with this one. 3G represents the third generation of mobile network technology, providing an information transfer rate of at least 144 kbit/s.
The network is based on standards established by the International Telecommunication Union. 3G networks were primarily applied for wireless voice calls, speedy mobile internet access, and mobile TV.
Most smartphones will still use this service when a stronger network is unavailable due to location or weak signal strength, demonstrating its strength as a modern standard of telecommunications.
H/H+
H and H+ network symbols mean that your device is using High Speed Packet Access, which means that you have 7.2Mbps download speed and 3.6Mbps average upload speed, roughly. This new technology, similar to EDGE, represents the transition in speed between 3G and 4G technology.
The first high speed packet access specifications supported peak speeds of 14Mbit/s download and 5.76Mbit/s upload, reducing latency and providing up to five times capacity in the downlink.
4G/LTE
4G, the fourth generation of mobile network technology, operating on another more advanced set of standards established by the International Telecommunication Union.
4G was another monumental standard, with peaks of 100Mbit/s download speed, while 3G and associated technologies offered peaks of up to 14Mbit/s.
LTE is the name for the worldwide standard for 4G networks. LTE networks use a different radio interface and certain core network improvements to boost network capacity and speed.
4G offered higher peak bit rates, new frequency bands, wider channel frequency bandwidth in Hertz, and a higher capacity for simultaneous data transfers.
As of 2021 4G represents 58% of the global mobile network market.
Pictured: a 5G mast
5G
5G, the fifth generation of mobile network technology, is the latest and most advanced standard of mobile network tech.
5G can provide download speeds up to 10 gigabits per second when the technology is fully implemented.
5G has also been touted as providing innovations in the often mentioned ‘internet-of-things’, in that the strength of the network can provide links between types of technology that could not have practically collected or delivered data with weaker network standards. For example, drones can connect to 5G networks and provide real time data in instances of natural disasters.
What will 5G do?
In theory 5G is supposed to increase the performance of your mobile data connection across the board: when it comes to download and upload speeds, latency, and reliability.
However, in reality, as of the current time, 5G has not had a particularly large impact. This is due to numerous factors. For example, 6G has largely remained concentrated in urban areas due to the technological demands required of the new generation of network, so those in the countryside cannot use the new network even if they’d like to.
This dissapointment may also have occured after many companies promised ultra fast speeds in slick marketing campaigns when the technology was still, in practice, essentially in its infancy and does not cover even close to the amount of the UK as is covered by the 4G and 3G networks.
What factors affect my signal strength?
External Factors
Various external factors can affect the speed of your mobile network connection, including:
Geographical Location
If you are in a remote area or in transit cell coverage may not be optimal or even available at all, resulting in greatly reduced network performance.
User Concentration
If you are in an area where many users are currently accessing the network your speeds will be greatly reduced. For example, if you are at a station after work waiting for the train at peak time and your mobile data is slow, the physical structure of the station itself is not slowing down your network speed, but the concentration of users all using the same access point.
Your Phone
The qualities of individual mobile phones can also affect the performance of your mobile network connection. Properties such as the network tech included in your device (the antenna, software, etc) will depend on age and vary thereby in terms of performance depending on how recently your device was released. It is also possible that accessories such as phone cases can interfere with the strength of your signal.
Common questions answered
Should I turn off mobile data when on Wi-Fi?
Modern mobile phones will automatically switch to a Wi-Fi network when one is available and you have the requisite credentials, so this is not essential in most instances.
However, the opposite is also true in that your device will automatically switch from a Wi-Fi connection to mobile data if the connection is lost, so if you have a limited data plan it is advisable to switch off mobile data entirely until the specific moments you need it, in order to avoid accidentally using up your data when your device automatically switches to mobile data.
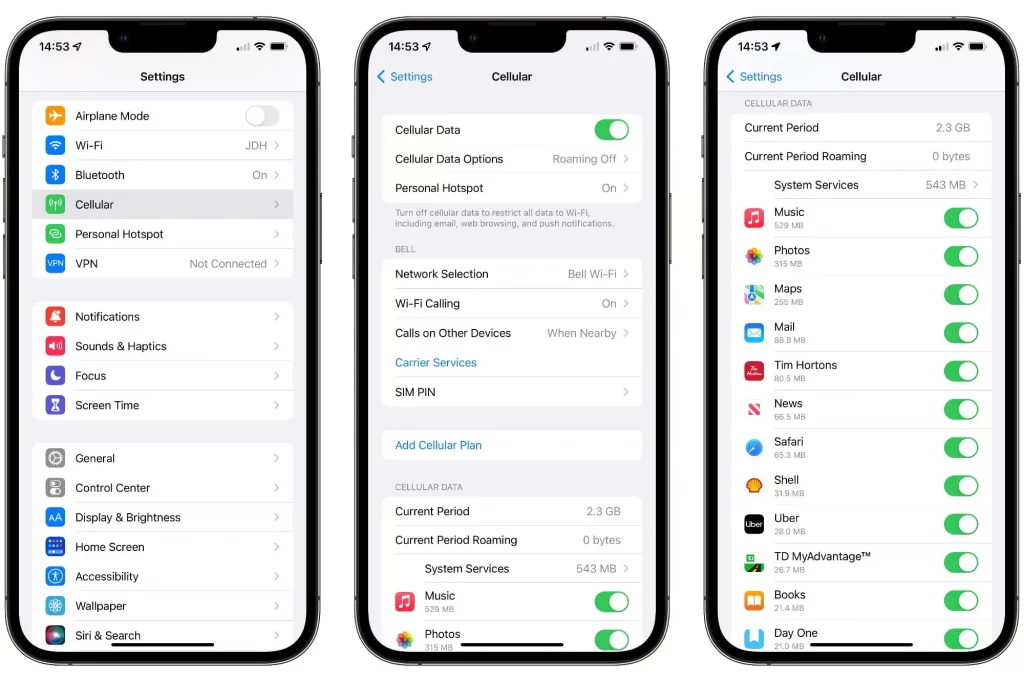
iOS and Android both offer various options to track your mobile data usage
Why is my mobile network not available?
See the above factors that affect signal strength.
What drains more battery, Wi-Fi or mobile data?
Using Wi-Fi is more power efficient than mobile data as the connection is consistent. When using mobile data, it is necessary for your device to constantly establish that the connection is still strong as it constantly varies, which is a much greater drain on the device than a consistent Wi-Fi connection.
Is mobile data secure?
Mobile data is certainly more secure than public Wi-Fi networks given that providers assure users that their data is encrypted and cannot be intercepted by outside parties.
What is the difference between 4G and H+?
H+ is often considered to essentially be ‘2.75G’. It is the stage in mobile network development between 2G and 3G, providing the groundwork for the implementation of 3G technology. Your device likely still uses the H/H+ network standard when struggling for signal.
Can mobile networks see your browsing history?
Yes, your browsing history is accessible to your mobile network provider.
If you are looking to upgrade your phone, perhaps to improve your mobile network performance, check out The Big Phone Store for the best refurbished phones and brand new devices from one of the UK’s most environmentally conscious tech retailers.
Other content from The Big Blog
Best Phones for the Elderly in 2022
How are Refurbished Phones Tested?
Upgrade today by selling your old device! Click on the links to find out value of your mobile phone and how to 'Sell My Phone,' benefit from 'Phone Trade-In' or 'iPhone Trade-In' for the best value.
-------------------------------